Galileo ground segment updates
June 17, 2024
The European Space Agency (ESA) has upgraded the ground segment of the Galileo satellite navigation system, without any disruption to its users.
Read More

The European Space Agency (ESA) has upgraded the ground segment of the Galileo satellite navigation system, without any disruption to its users.

Nearly all satellites are highly vulnerable to cyberattacks, ground- or space-based lasers, high-powered microwaves, the debris field from a destroyed satellite and the radiation produced by a nuclear explosion in space.

The European Space Agency (ESA) has selected Syntony GNSS to supply user demonstration receivers for its low-Earth orbit positioning, navigation and timing (LEO-PNT) project.
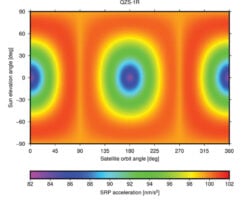
In early 2015, the Navigation Support Office of the ESA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) began a collaboration. The ESA-JAXA collaboration is designed to cross-validate Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) Precise Orbit Determination (POD) results and share expertise to improve the POD accuracy of QZSS.

Earth is experiencing a severe solar storm causing concern for those responsible for power grids, communication systems and satellites. NOAA has reported measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm that has been visible as aurora across vast swathes of the Northern Hemisphere.

Syntony GNSS has partnered with Keysight Technologies, an RF testing solutions manufacturer, to advance GNSS testing and simulation capabilities.

On April 27, 2024 the SpaceX Falcon 9 medium-lift launch vehicle launched into orbit Galileo satellites GM25 and FM27 from Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This was Falcon 9’s 20th and final launch.

NextNav has petitioned the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to add a new spectrum solution in the Lower 900 MHz band (902-928 MHz band) to complement and backup GPS.
Follow Us